Northern California Ganglion & Mucous Cyst Treatment
Treatment for Ganglion & Mucous Cysts in Northern California
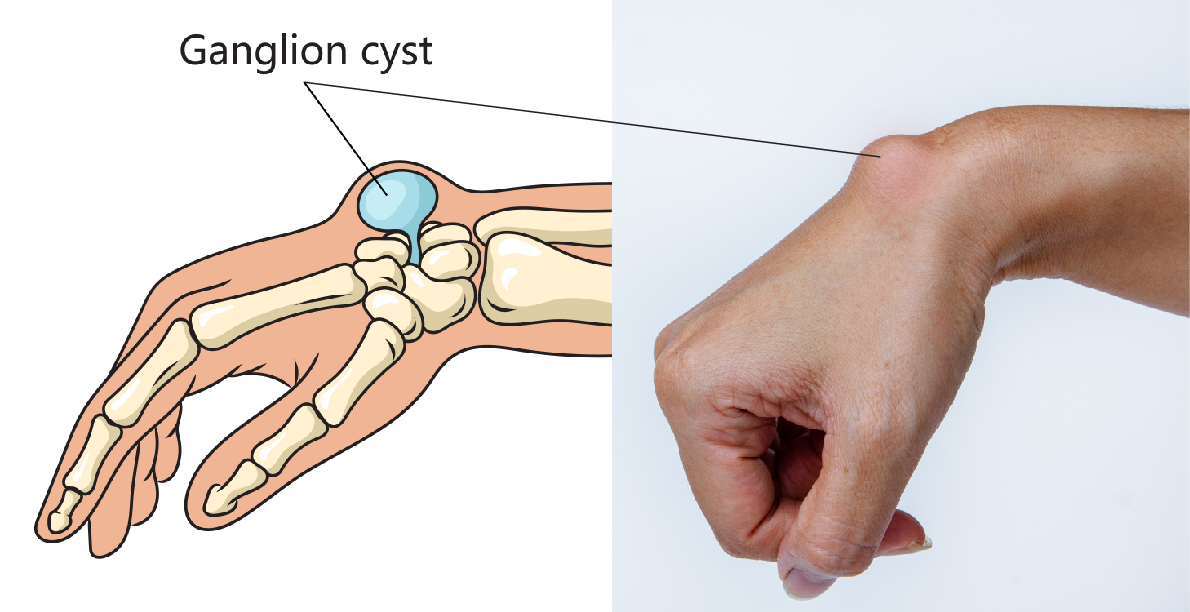
Ganglion cysts are non-cancerous lumps that typically develop near joints or tendons, most commonly on the back of the hand or wrist. These cysts are filled with a gel-like fluid, and they can vary in size from small to relatively large. Mucous cysts are usually benign and not a cause for immediate concern, but they can cause discomfort or restrict movement in some cases.
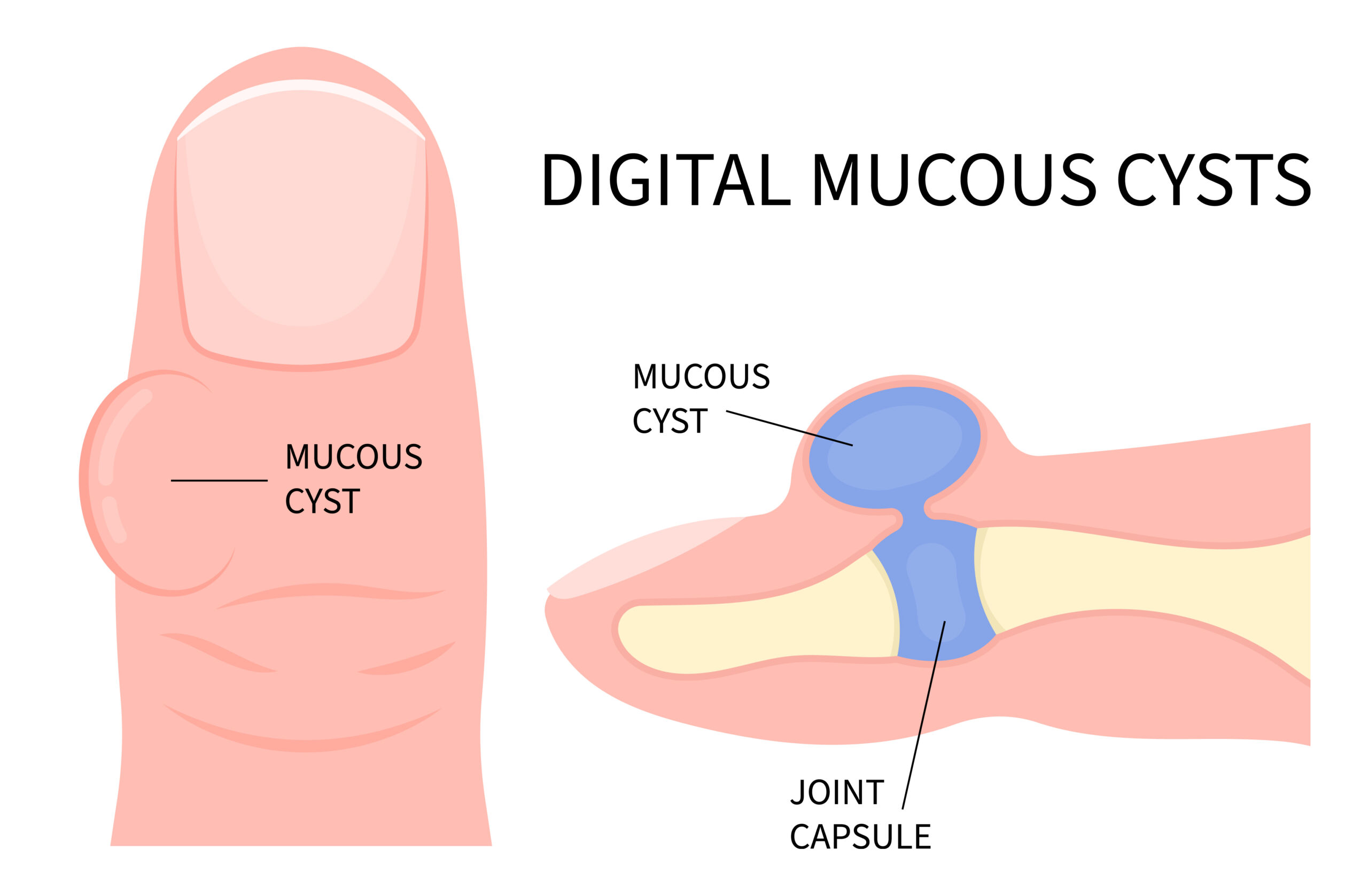
Mucous cysts are a subtype of ganglion cyst that typically develop in the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints, or the first joint of the fingers at the tip, just before the fingernail starts.
Causes
The exact cause of ganglion and mucous cysts is not fully understood. However, they often result from the degeneration of connective tissue or the synovial sheath surrounding a joint or tendon. When this tissue weakens or breaks down, the fluid accumulates, leading to the formation of the cyst.
Nonsurgical Treatments
In some cases, ganglion cysts can be managed without the need for surgery. Nonsurgical treatment options include:
- Observation: If the cyst is small, painless, and not causing any functional impairment, your doctor may choose to monitor it over time to see if it resolves on its own.
- Immobilization: Wearing a brace or splint can help rest the affected hand or wrist, reducing inflammation and pressure on the cyst.
- Aspiration: A procedure called aspiration involves draining the fluid from the cyst using a needle and syringe. This can provide temporary relief, but there is a risk of recurrence.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injecting corticosteroids into the cyst can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, although this is also a temporary solution.
Surgical Treatments
If the cyst becomes painful, significantly impacts hand function, or other treatments have been ineffective, surgical intervention may be recommended. Surgical options include:
- Cyst Excision: This involves the complete removal of the cyst, along with its connection to the joint or tendon sheath. This is typically performed as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia.
- Ganglion/Mucous Cyst Open Surgery: This traditional surgical approach involves making an incision over the cyst and removing it. The surgeon may also remove a small portion of the nearby joint capsule or tendon sheath to reduce the chances of recurrence.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: In some cases, a minimally invasive technique called arthroscopy can be used to remove the cyst. This involves using a small camera and specialized instruments inserted through tiny incisions.
Citations:
- Chen AC, Hsu YC, Lin JY, Yang TH. Ganglion Cysts of the Hand and Wrist: Clinical Features and Surgical Outcome. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7589. Published 2018 May 15. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-25800-w
- Tomaino MM. Ganglion Cysts of the Hand and Wrist. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1999 Nov-Dec;7(6):231-8. doi: 10.5435/00124635-199911000-00002. PMID: 10797324.
