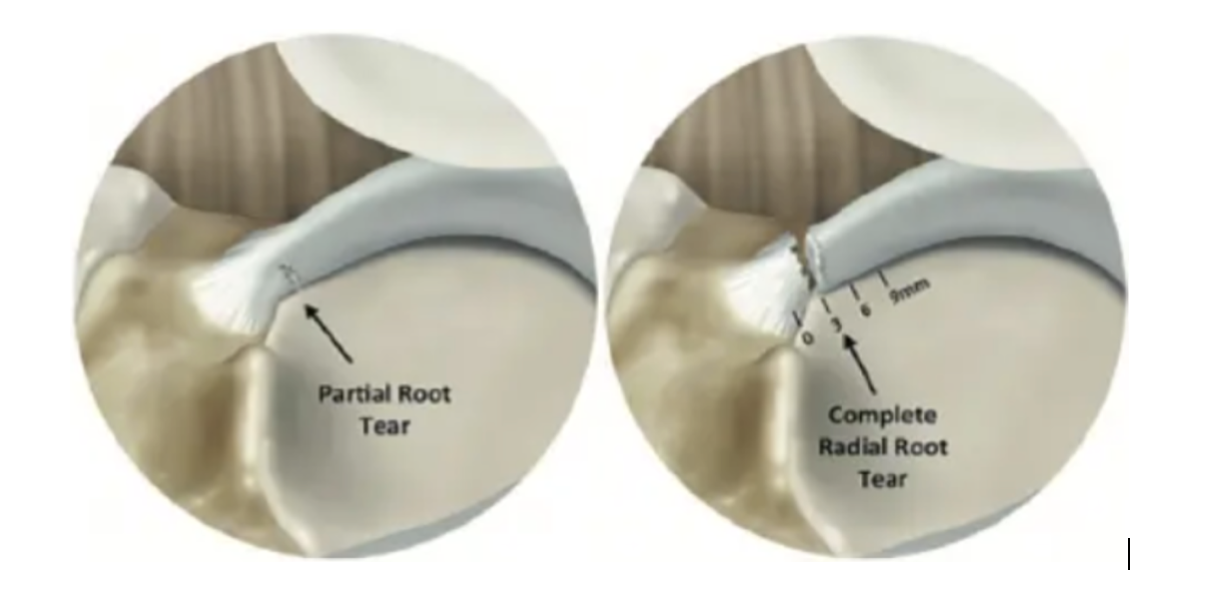
A meniscus root tear is a type of knee injury that affects the meniscus, a C-shaped cartilage structure located in the knee joint. The meniscus has two roots that anchor it to the tibia (shinbone), and when these roots are torn or detached, it is referred to as a meniscus root tear. This injury can cause significant pain and functional impairment in the knee.
Causes
Meniscus root tears are typically caused by traumatic injuries or degenerative changes in the knee joint. Some common causes include:
- Acute trauma: A sudden, forceful twisting or pivoting movement of the knee joint, often seen in sports activities or accidents, can lead to a meniscus root tear.
- Degenerative changes: Over time, the meniscus can weaken and degenerate due to age-related wear and tear. This can make it more susceptible to tearing, even with minimal force or stress on the knee joint.
“Even a deep squat can increase the risk of meniscus root tear,” says Dr Semon Bader of Golden State Orthopedics & Spine. “The posterior aspect of the meniscus gets a lot of pressure and as we age the tissue can tear, particularly with extreme movements. But it can happen with simple twisting or pivoting, too.”
Symptoms
The symptoms of a meniscus root tear can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain is typically felt along the joint line of the knee, particularly at the inner or outer side, depending on which meniscus is affected.
- Swelling: The knee joint may become swollen, tender, and warm to the touch due to inflammation caused by the injury.
- Clicking or popping: You may experience clicking or popping sensations in the knee joint during movement.
- Locking or catching: The torn meniscus root can sometimes get caught in the knee joint, causing the knee to lock or catch, limiting your ability to fully extend or flex the knee.
- Instability: You may feel a sense of instability in the knee, as the torn meniscus can affect the joint’s stability and balance.
Treatment
The treatment options for meniscus root tears depend on various factors, including the severity of the tear, the patient’s age, activity level, and overall knee health. Here are some common treatment approaches:
- Conservative treatment: For minor tears or tears in older individuals with minimal symptoms, conservative treatment may be recommended. This can include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) therapy, along with the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy may also be prescribed to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve stability.
- Surgical repair: In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, especially for younger individuals or athletes. The goal of surgery is to reattach or repair the torn meniscus root. This can be done through arthroscopic surgery, where small incisions are made in the knee, and specialized instruments are used to visualize and repair the meniscus.
- Meniscus transplantation: In cases where the meniscus root tear cannot be repaired, a meniscus transplantation may be considered. This involves replacing the damaged meniscus with a donor meniscus or a synthetic implant to restore knee function.
“If you injure your knee and x-rays do not show advanced arthritis, get an MRI,” Dr Bader advises. “Early diagnose of a meniscus root tear and early treatment with repair has the best prognosis.”

It’s important to consult with a medical professional, such as an orthopedic surgeon or sports medicine specialist, for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.


